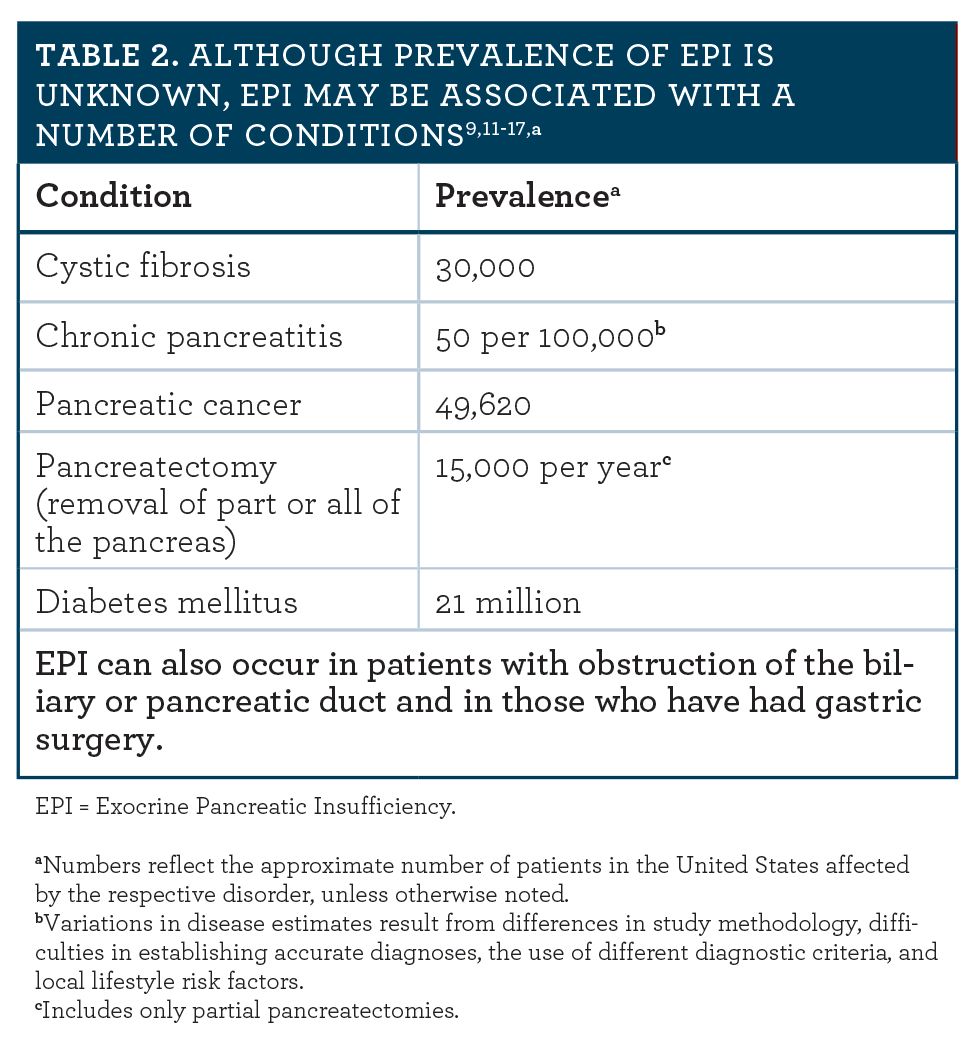
EPI is associated with certain diseases and conditions that affect the pancreas Some of these diseases you are born with, like cystic fibrosis, while others may occur Read MoreTest Usage Pancreatic elastase (PE) is not degraded during intestinal transit and the concentration of PE in a stool sample reflects exocrine pancreatic function This assay allows the diagnosis or exclusion of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, which can be caused by chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic tumor, cholelithiasis orDr Rudert answers questions on this often misdiagnosed disorder What are the symptoms of EPI (Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency)?
Endoscopic Pancreatic Function Testing Epft In Children A Position Paper From The Naspghan Pancreas Committee
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency stool test
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency stool test-Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) in patients with chronic pancreatitis (CP) leads to many debilitating symptoms and nutritional deficiencies 1–3 Patients with EPI may have symptoms related to maldigestion, as well as nutritional deficiencies (ie, fatsoluble vitamins A, D, E, and K), micronutrient deficiencies, and an overall state of malnutrition 2 Symptoms related to Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency ( EPI ) is a disorder caused by a lack of certain digestive enzymes, which are needed to extract important nutrients from




Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency In Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes More Common Than You Think Semantic Scholar
Stool Test Markers for Bile Acid Malabsorption & Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Diagnosis Fecal steatocrit and elastase1 can easily help diagnose Bile Acid Malabsorption (BAM)—which is also called bile acid diarrhea—and Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) The previous gold standard test for bile acid malabsorption was a fecal fat test, which asked patientsSymptoms of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Cats who have feline pancreatitis often display the same symptoms and follow the same patterns The affected cats will seem extremely hungry, even though they are constantly eating Cats who have feline pancreatitis will lose weight and have high amounts of stool that can be loose and strong in odorPeople with EPI have a particularly difficult time absorbing fats from foods This leads to uncomfortable digestive problems, such as Abdominal pain, gas and bloating Constipation Diarrhea Fatty stools (pale, oily, foulsmelling poop that floats)
Dr Cynthia Rudert, Celiac Disease and Gluten Intolerance expert answers your questions on celiac 5 million emergency room visits in the US are for diarrhea and abdominal pain If you have chronic symptoms, could it be EPI?Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to properly digest food due to a lack of digestive enzymes made by the pancreasEPI is found in humans afflicted with cystic fibrosis and Shwachman–Diamond syndrome, and is common in dogsEPI is caused by a progressive loss of the pancreatic cells that make digestive enzymes;Foulsmelling, greasy stools (steatorrhea) Weight loss One may also ask, can exocrine pancreatic insufficiency disappear?
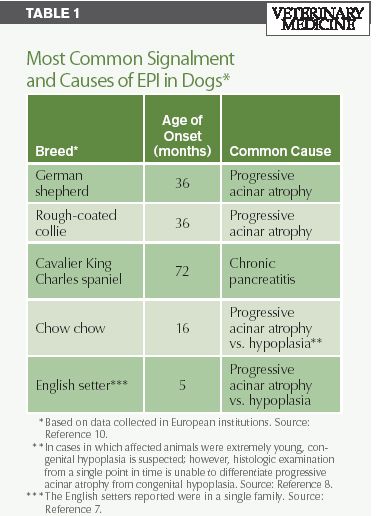
Typically, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in the GSD is presented in young adult dogs between 1 to 5 years of age The diagnosis of EPI needs to be confirmed by use of laboratory tests Diarrhea and foul smelling feces due to high fat content results and because all the food ingredients are not being digested completely the German ShepherdEPI can make mealtime difficult EPI is when someone can't digest their food normally because their pancreas isn't making enough enzymes The enzymes help break down the food you eat so it can be absorbed into your body If your body isn't making enough pancreatic enzymes, this can result in not being able to digest food properly, or maldigestionLoss of digestive enzymes leads to maldigestion




Pin On Health



Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Pei Canadian Digestive Health Foundation
What are the symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)? Elastase is an enzyme made by the pancreas that helps down essential nutrients like fats, proteins, and carbohydrates after you eat If little or no elastase is found in the stool, it might mean the enzyme is not working properly and thus your doctor might diagnose you with Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In adults, pancreatic insufficiencyThis test measures the amount of elastase, an enzyme produced by the pancreas, in your stool A deficiency of elastase could be an indicator of EPI It may be harder to diagnose milder EPI using this test Your doctor may not use this test if you have diabetes




Management Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Children Sankararaman 19 Nutrition In Clinical Practice Wiley Online Library



Endoscopic Pancreatic Function Testing Epft In Children A Position Paper From The Naspghan Pancreas Committee
Fat maldigestion due to EPI can lead to gas, bloating, and stomach pain Foulsmelling, greasy stools (steatorrhea) Steatorrhea is a type of bowel movement that is oily, floats, smells really bad, and is difficult to flushP < or = 0001) The symptoms of EPI are similar to many other digestive conditions However, if you have unexplained weight loss, diarrhea, and fatty stools, there's a good chance that EPI
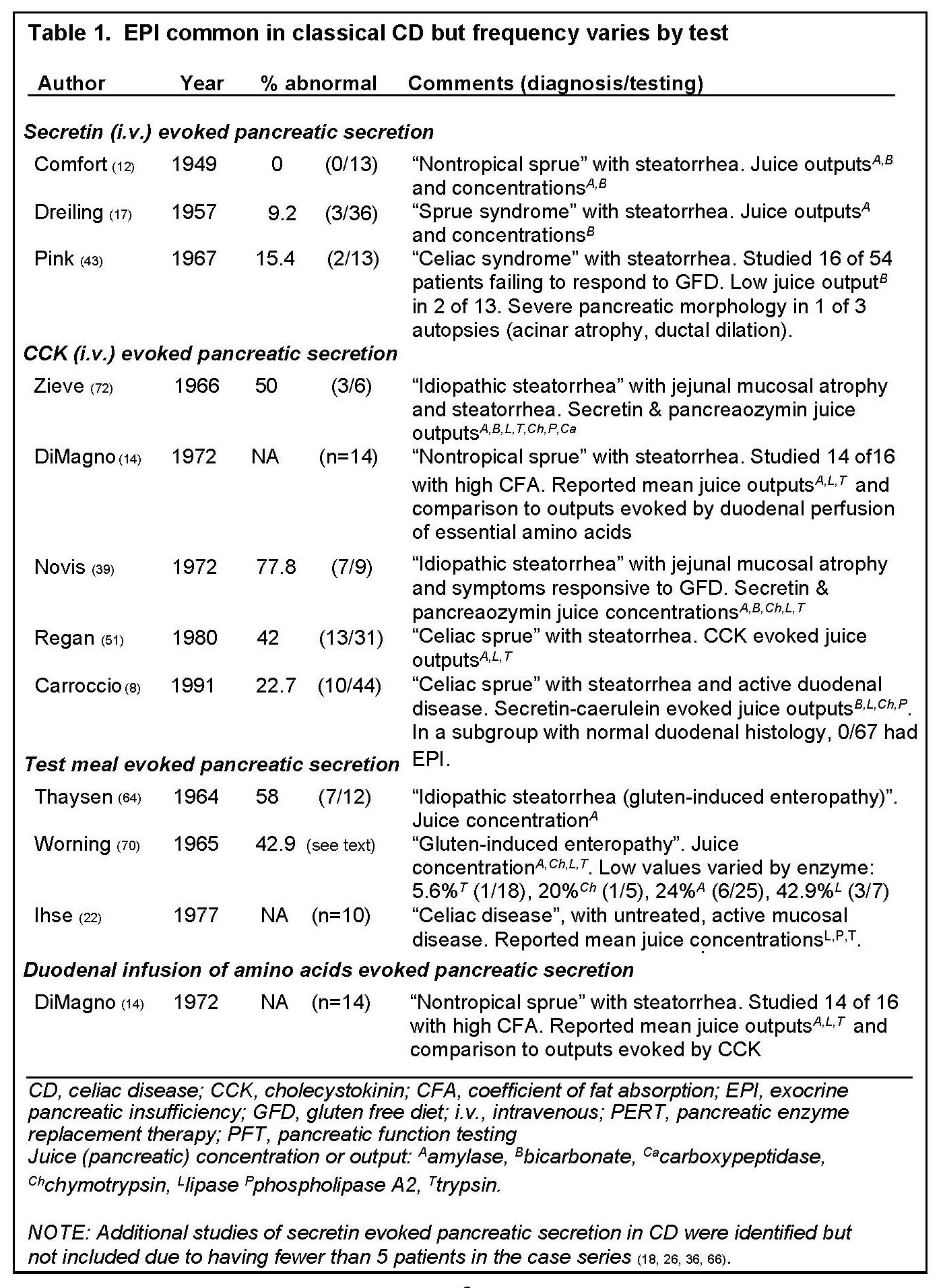



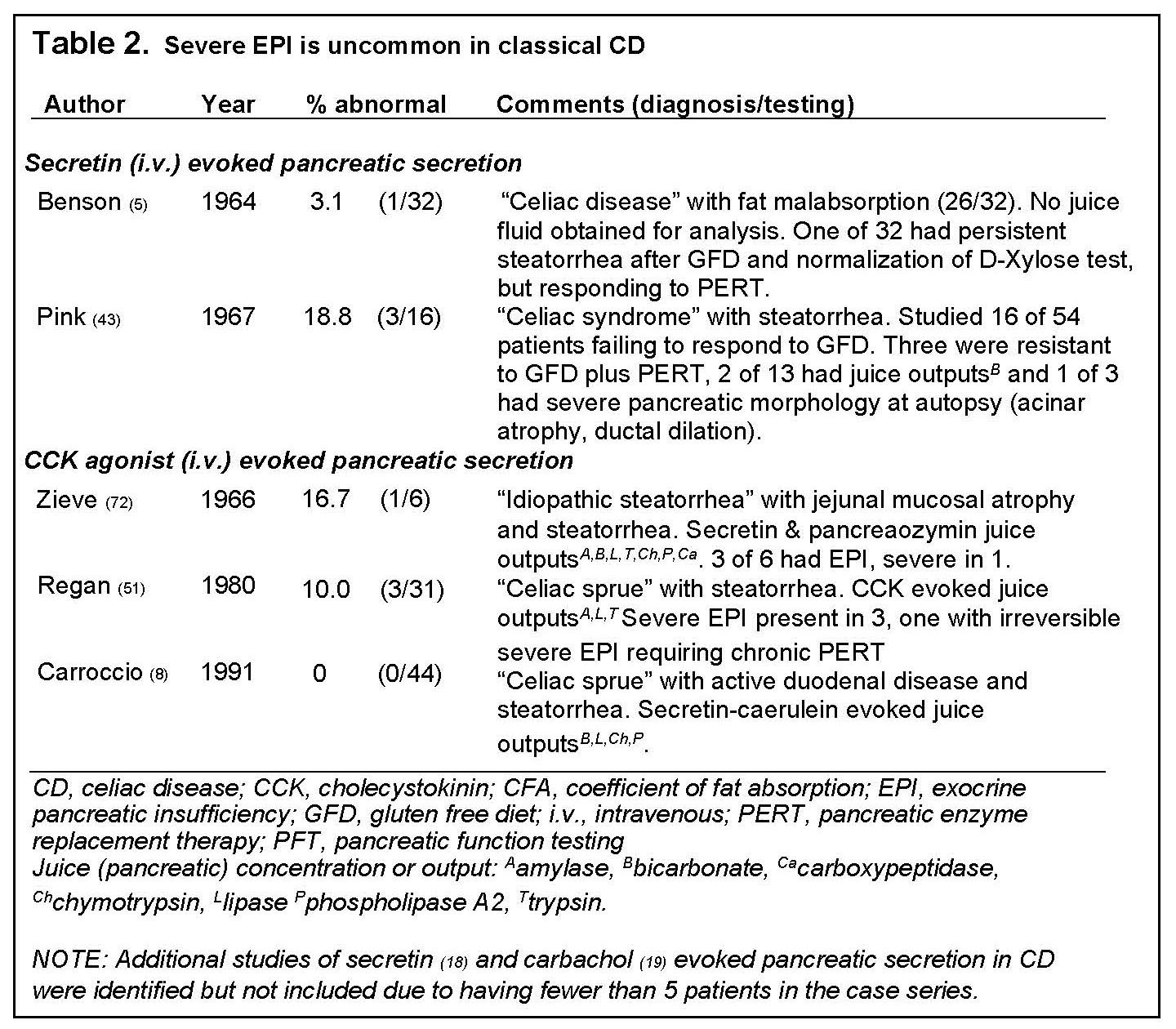
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency And Pancreatitis Associated With Celiac Disease Pancreapedia



P Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy A Concise Review P Insight Medical Publishing
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) is defined as partial or complete loss of digestive enzyme and bicarbonate secretion In chronic pancreatitis this is caused by a progressive destruction of functioning pancreatic tissue The overt clinical symptoms of PEI are steatorrhoea, weight loss and abdominal discomfort due to maldigestion Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is defined by a deficiency of exocrine pancreatic enzymes resulting in an inability to maintain normal digestion This inadequate digestion with nutrient and, especially, fat malabsorption occurs when intraduodenal levels of lipase fall below 5–10% of normal enzyme output 1 , leading to pancreatic steatorrhea, weight loss, and aExocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a condition characterized by deficiency of the exocrine pancreatic enzymes, resulting in the inability to digest food properly, or maldigestion Who gets EPI?




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Market
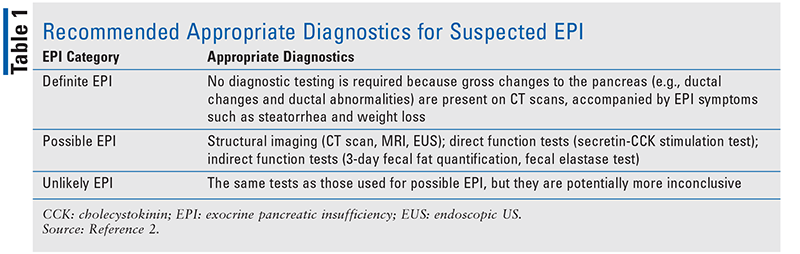



Lesson Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can be classified into mild, moderate, or severe Mild insufficiency occurs with reduced secretion of one or two enzymes with preserved bicarbonate and normal fecal fat Moderate insufficiency includes the above with impaired bicarbonate secretion Severe insufficiency occurs when all of the above plus steatorrheaExocrine pancreatic insufficiency develops in 50–80% of adults after a diagnosis of 56 to 131 years 74, 75 The exact prevalence of EPI in pediatric CP is unknown, but 34% of children with CP in the INSPPIRE cohort were exocrine pancreatic insufficient at the time of enrollment 43 Typically, the diagnosis of CP is made prior to theThe pancreas works normally, but because ofinflammation and damage to the intestines, it may not secreteenzymes in the way it should If you switch to a glutenfreediet,



Acg Eposter Hall




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Dogs Clinician S Brief
If little or no elastase is found in the stool, it might mean the enzyme is not working properly and thus your doctor might diagnose you with Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In adults, pancreatic insufficiency is often a sign of chronic pancreatitisExocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a condition that can occur when the pancreas is unable to make the digestive enzymes it should As a result, your body isn't able to digest food into nutrients such as fats, proteins, and carbohydratesExocrine pancreatic insufficiency is an under recognized complication of pancreatic disease 13 While patients with advanced exocrine pancreatic insufficiency usually present with abdominal pain and steatorrhea, those with less severe insufficiency may only have mild symptoms This topic will review the etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of exocrine pancreatic




The Prevalence And Impact Of Low Faecal Elastase 1 In Community Based Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes Research And Clinical Practice



A Quick Review Of Canine Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
WebMD explains exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI), a condition in which the pancreas isn't producing enough enzymes to break down and absorb nutrients Skip to The most common signs and symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency include Frequent gas and/or abdominal bloating Abdominal pain, cramps (the pain is sometimes referred to as "epigastric" because it occurs in the upper middle part of Unexplained weight loss (inability to gain weight inPancreatic exocrine insufficiency can follow major pancreatic resection and result in the malabsorption of fat, causing symptoms of steatorrhea, abdominal pain and weight loss The extent of malabsorption will depend on the original disease process




Causes Of Pancreatic Insufficiency Download Table




Pdf Poor Diagnostic Values Of Stool Analysis And Steatocrit Test In Detecting Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Semantic Scholar
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is characterized by a deficiency of exocrine pancreatic enzymes, resulting in malabsorption Numerous conditions account for the etiology of EPI, with the most common being diseases of the pancreatic parenchyma including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and a history of extensive necrotizing acute pancreatitisCOMPONENT DESCRIPTION TEST TYPE INFECTIOUS UNIT OF MEASURE NUMERIC MAP LOINC Pancreatic Elastase, Fecal Resultable N ug/g XXX For questions regarding the Interface Map, please contact interfacesupport@aruplabcomA primer on exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, fat malabsorption, and fatty acid abnormalities Am J Manag Care 17;23(12)(suppl)S3S9 Durie P, Baillargeon JD, Bouchard S, Donnellan F, ZepedaGomez S, Teshima C Diagnosis and management of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) in primary care consensus guidance of a Canadian expert




3 Ways To Diagnose Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Wikihow



Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy A View From Behind The Counter
Introduction Identification of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) is important in the management of chronic pancreatitis The 72h stool for fecal fat estimation (FFE) has long been considered a gold standard indirect test for the diagnosis of PEI However, the test is cumbersome for both patients and laboratory personnel alikeStool elastase was expressed as normal (>0 microg/gram stool), moderately reduced (1000 microg/gram), or severely reduced (78%;Pancreatic elastase concentrations above 0 mcg/g are normal and are not indicative of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency Pancreatic elastase concentrations from 1000 mcg/g are suggestive for moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency Pancreatic elastase concentrations below 100 mcg/g are consistent with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency




Basics Of Pancreatitis And Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency




Elastase Gutsandgrowth
A blood serum TLI test (trypsinlike immunoreactivity) showing a concentration of ≤25 mcg/L in dogs or ≤80 mcg/L in cats means they have Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency There is also a test for the presence of a pancreatic enzyme called elastase in the stoolTalking to Your Doctor About Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency If you have been experiencing a long period of bloating, excess gas, stomach pain, and oily stools, it is time to talk to your doctor There are many different gastrointestinal conditions that could cause these and other similar symptoms, and it is crucial to get an accurate diagnosisExocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to produce sufficient pancreatic enzymes to digest fats, carbohydrates, and proteins This difficulty in digestion leads to poor absorption of nutrients which commonly causes weight loss despite a normal or increased appetite Affected dogs often have large volumes of pale, fatty feces




Diagnostic Performance Of Measurement Of Fecal Elastase 1 In Detection Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Clinical Gastroenterology And Hepatology




Pdf Faecal Elastase 1 Not Helpful In Diagnosing Chronic Pancreatitis Associated With Mild To Moderate Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Stool levels of elastase and chymotrypsin are the tests used to determine pancreatic digestive function When stool elastase levels are below 0 ug/mL, a diagnosis of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency is made Fun fact – elastase is an enzyme unique to the human pancreas Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI or PEI) The major symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) include steatorrhea and weight loss The most common symptomatic complaint is diarrhea, which isExocrine pancreatic insufficiency is caused by decreased production of digestive enzymes by the pancreas The most common clinical signs are polyphagia, weight loss, and a large volume of loose stools Diagnosis is made by measurement of serum trypsinlike immunoreactivity Treatment includes supplementation of pancreatic digestive enzymes and




Pdf Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




A Primer On Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Fat Malabsorption And Fatty Acid Abnormalities
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) develops when your pancreas doesn't make or deliver enough of those enzymes That enzyme shortage makes it difficult for your body to convert food intoRegardless of its cause, the signs associated with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are usually obvious and fit a distinct pattern The cat loses weight, seems constantly hungry, and has high volumes of loose or semiformed stools The stool may have a foul odor The high amount of fat in the stool may make the anal area and coat appear greasyIn individuals with pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, the pancreas doesn't make enough digestive enzymes to adequately break down food into absorbable components




Pdf Poor Diagnostic Values Of Stool Analysis And Steatocrit Test In Detecting Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Semantic Scholar




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Prevalence Diagnosis And Manageme Ceg
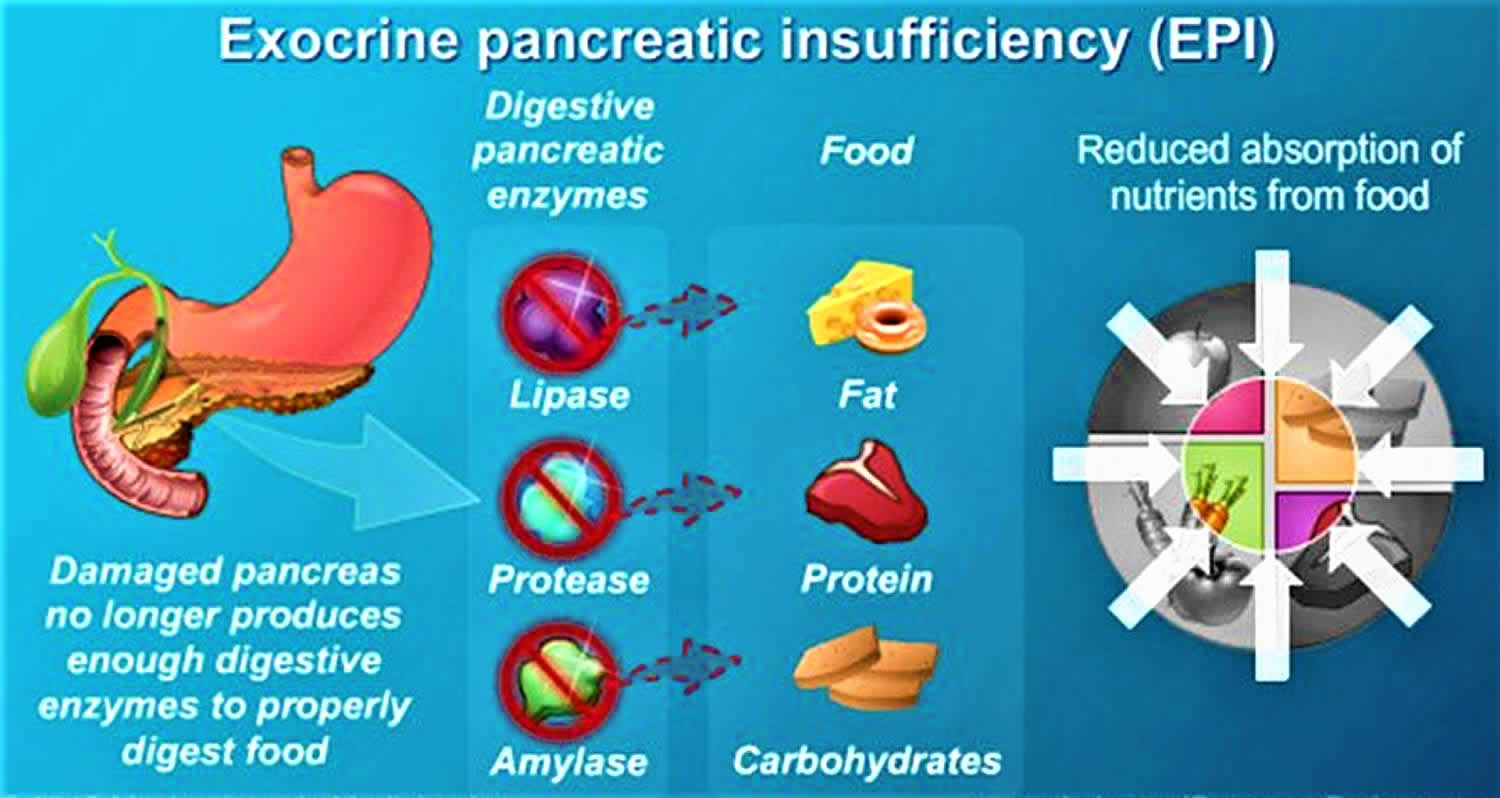
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency occurs when the amount of enzymes released and transported to the small intestine is inadequate for proper food digestion and absorption of nutrients Any condition that blocks the pancreatic ducts or damages or destroy the cells that produce elastase can cause pancreatic insufficiency



3
/exocrine-pancreatic-insufficiency-4177936-821-618578bea845406fa96c78167aff8657.png)



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Symptoms Causes And Diagnosis



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency And Pancreatitis Associated With Celiac Disease Pancreapedia



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment




Symptoms Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi Treatment
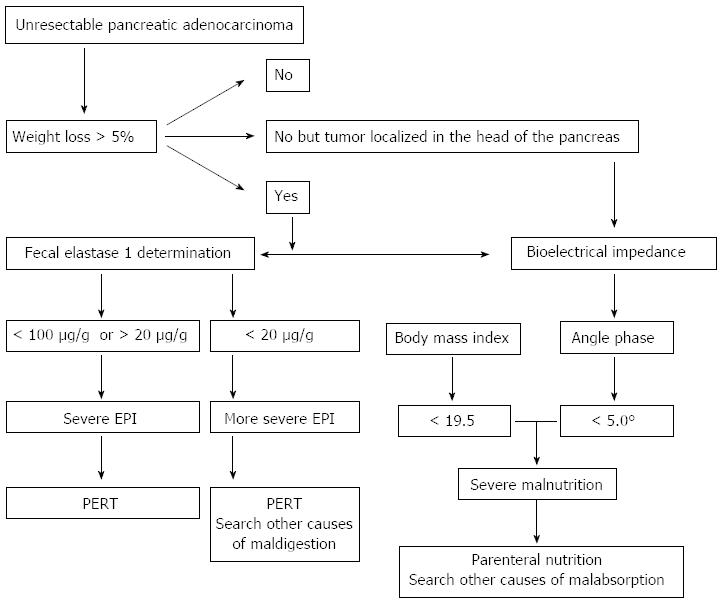



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




How To Diagnose Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency How To




Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Guideline Working Party Guideline Algorithm Guidelines




Pdf Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Semantic Scholar




Figure 4 From Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In The Cat Semantic Scholar




Introduction And Practical Approach To Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency For The Practicing Clinician Othman 18 International Journal Of Clinical Practice Wiley Online Library




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Dogs Vca Animal Hospital




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency




Diagnosis Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency From Stool Fat And Weight Springerlink




Undiagnosed Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency And Chronic Pancreatitis In Functional Gi Disorder Patients With Diarrhea Or Abdominal Pain Talley 17 Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Wiley Online Library




What Is Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Everyday Health




Effects Of Deficiency Of Exocrine Pancreatic Secretion




Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Pei And Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy Pert Guts Uk




Slide Show Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi




Diagnosis Exclusion Of Canine Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi




Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy Dr Seyed Ali Jafari



1
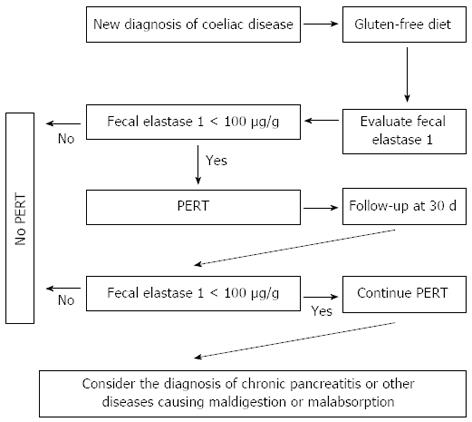



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Humans Identify Epi




References In How Useful Is Fecal Pancreatic Elastase 1 As A Marker Of Exocrine Pancreatic Disease The Journal Of Pediatrics




Pdf Less Common Etiologies Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Semantic Scholar




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Veterian Key




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Beating Pancreatitis




Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Pei Canadian Digestive Health Foundation



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi Pipeline Insight




Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency After Gastrointestinal Surgery Hpb
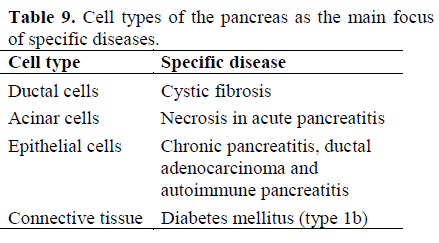



Giessen International Workshop On Interactions Of Exocrine And Endocrine Pancreatic Diseases Insight Medical Publishing
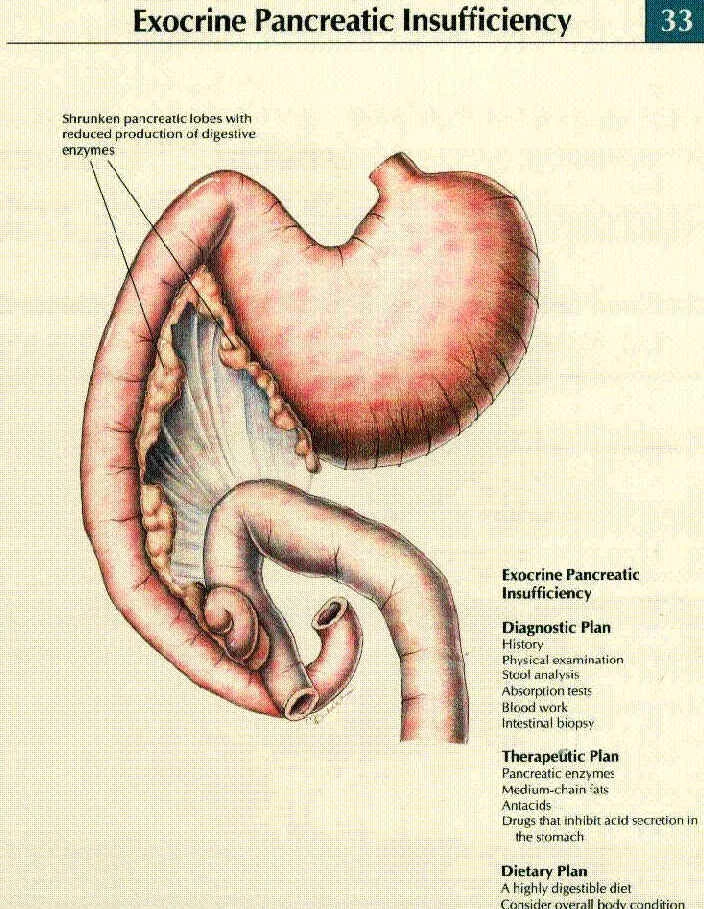



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Canine Diabetes Wiki Fandom
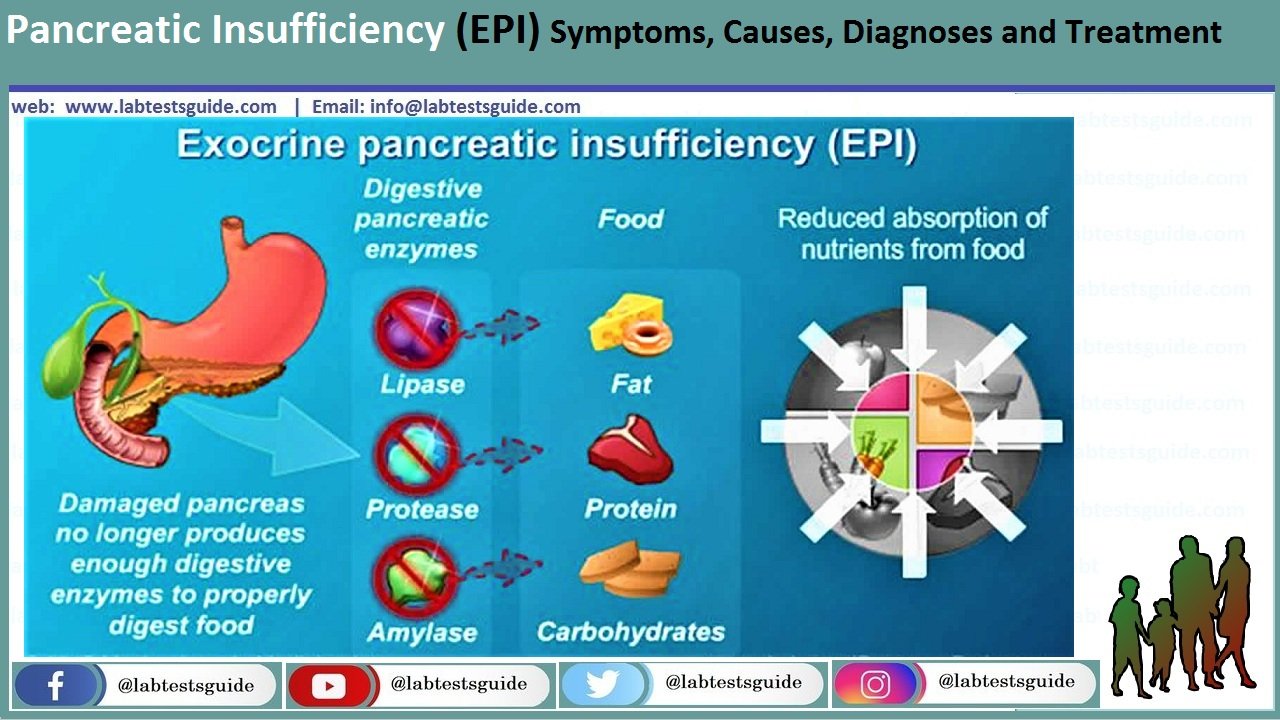



Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi Symptoms Causes Diagnoses And Treatment Lab Tests Guide




Estimation Of Faecal Elastase 1 And Faecal Chymotrypsin In Patients Download Table




Symptoms Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Everyday Health
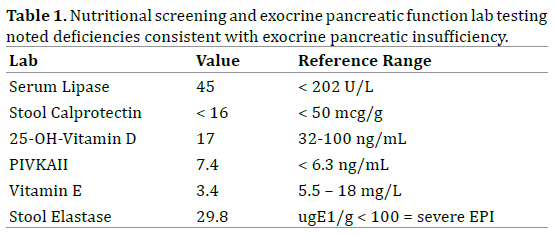



Johanson Blizzard Syndrome Expanding The Phenotype Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Insight Medical Publishing




Epi4dogs Poop Chart Managing Epi Non Profit Educational Resource Forum



2




Get The Scoop What Your Pet S Poop Is Telling You
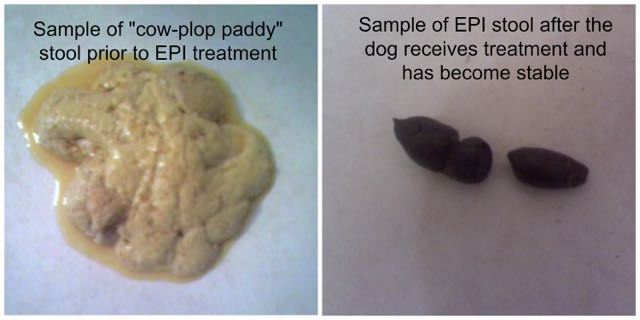



Epi4dogs Practice For O Managing Epi Non Profit Educational Resource Forum




Diagnose And Treat Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency In Diabetes Implementing Guidelines Guidelines In Practice




Practical Guide To Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Breaking The Myths Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Pancreatic Function Tests D Functional Anatomy Of The Pancreas The Functional Unit Of Pancreas Is Acinus Its Draining Ductule The Duct Epithelium Ppt Download




Slide Show Understanding Nutrition And The Role And Benefits Of Pert
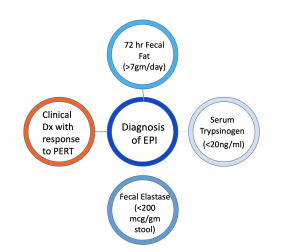



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Mission Cure




How To Diagnose Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency How To
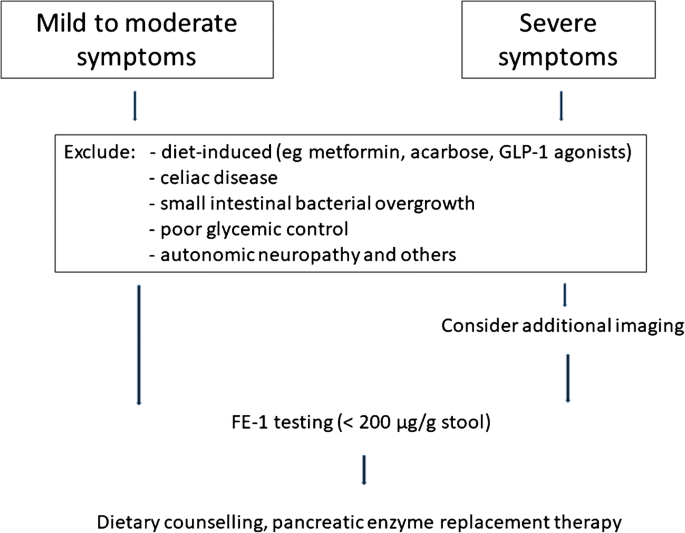



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Springerlink




Introduction And Practical Approach To Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency For The Practicing Clinician Othman 18 International Journal Of Clinical Practice Wiley Online Library
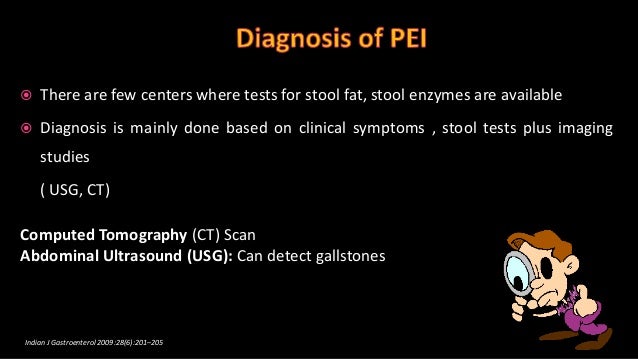



Basics Of Pancreatitis And Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency
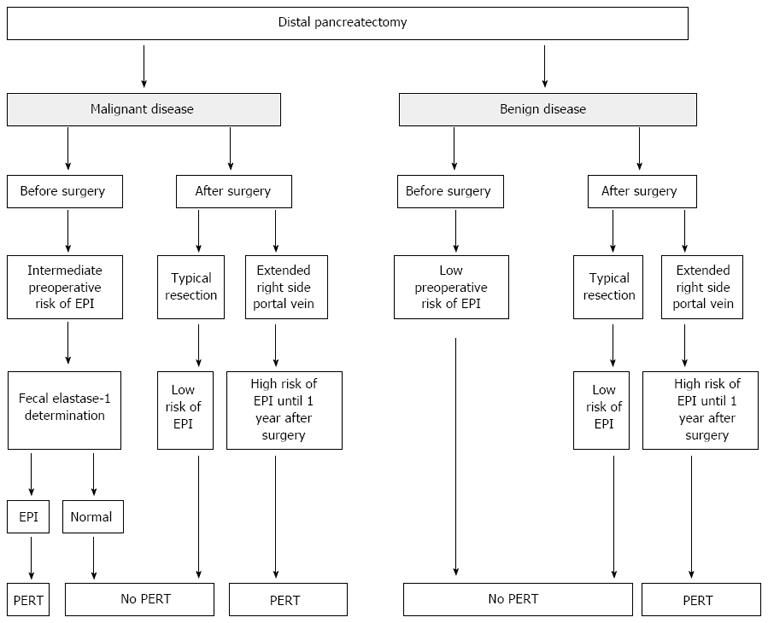



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




What Is Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Everyday Health




The Long Road To My Epi Diagnosis Everyday Health




Do You Have Epi Or Something Else Everyday Health




Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Clinical Gastroenterology And Hepatology




Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency In Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes More Common Than You Think Semantic Scholar




Epi Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Symptoms Treatment And More




3 Ways To Diagnose Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Wikihow



Plos One Feasibility Of Fecal Micrornas As Novel Biomarkers For Pancreatic Cancer




Severe Impaired Deambulation In A Patient With Vitamin D And Mineral Deficiency Due To Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Insight Medical Publishing




A Primer On Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Fat Malabsorption And Fatty Acid Abnormalities
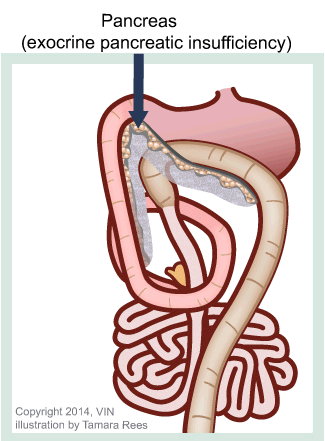



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Mar Vista Animal Medical Center




Pdf Poor Diagnostic Values Of Stool Analysis And Steatocrit Test In Detecting Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Semantic Scholar




What Is Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Ben S Natural Health




When To Consider The Pancreas
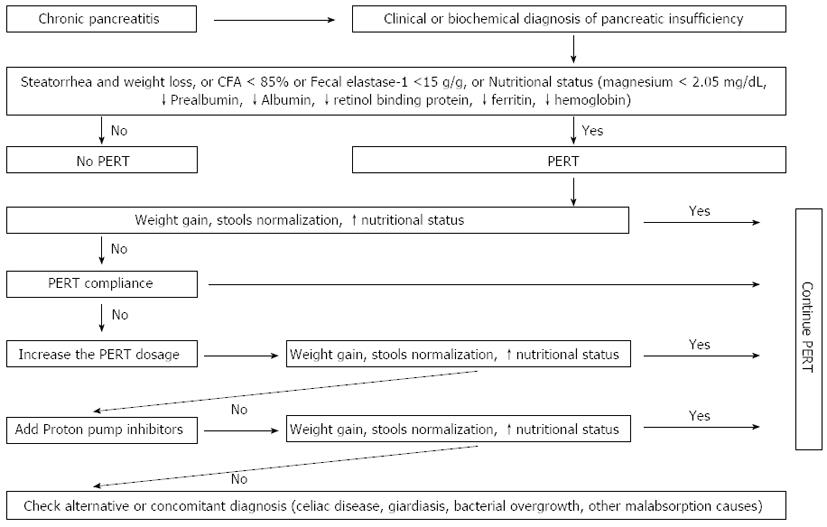



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas



Pancreatic
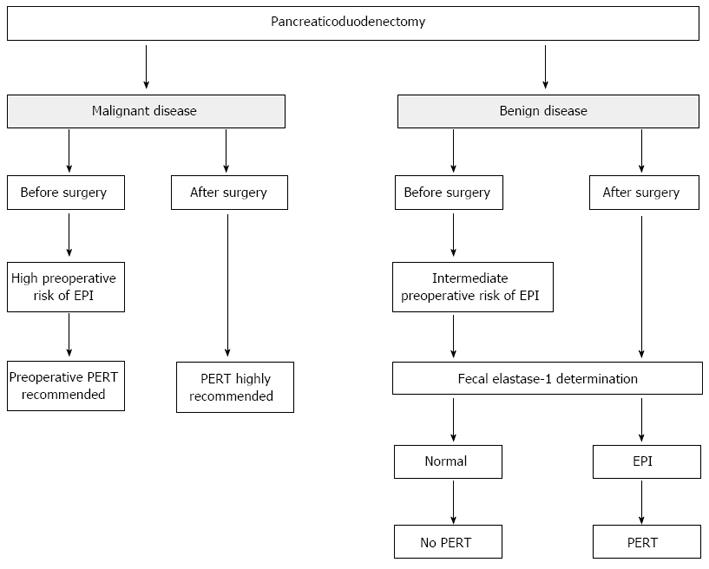



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




A Double Blind Randomized Multicentre Crossover Study To Prove Equivalence Of Pancreatin Minimicrospheres Versus Microspheres In Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Halm 1999 Alimentary Pharmacology Amp Therapeutics Wiley Online Library




Symptoms And Tests Used In The Diagnosis Of Exocrine Pancreatic Download Table




Introduction And Practical Approach To Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency For The Practicing Clinician Othman 18 International Journal Of Clinical Practice Wiley Online Library




Epi And Other Digestive Diseases In Dogs Dogs Naturally



Skin Signs Of




Diagnosis Exclusion Of Canine Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Epi




Indirect Diagnostic Tests For Evaluating Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Download Table
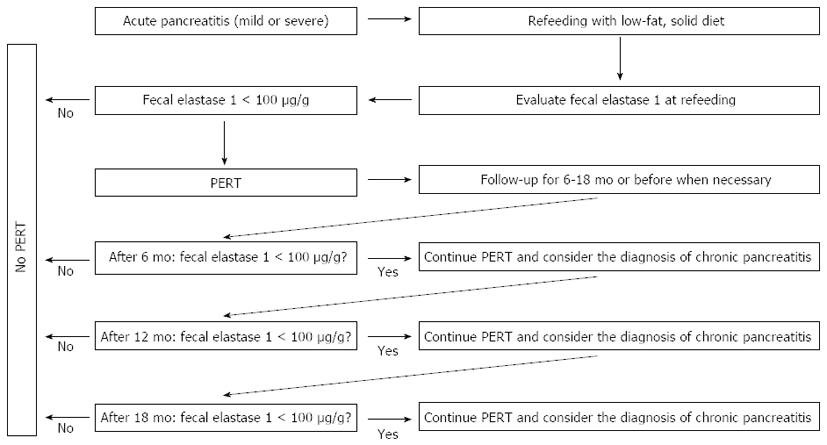



Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency In Adults A Shared Position Statement Of The Italian Association For The Study Of The Pancreas




Pancreatic Insufficiency An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Who S At Risk Of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Infographic Everyday Health




Global Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Market By Markettrends Issuu



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿